Fundamentals – HEIDENHAIN ND 720 v.3 User Manual
Page 4
4
Y
X
Z
+Y
+X
+Z
–Z
–Y
–X
Datum or
origin
Graduation
Fundamentals
Fundamentals
You can skip this chapter if you are already familiar with
coordinate systems, incremental and absolute dimensions,
nominal positions, actual positions and distance-to-go.
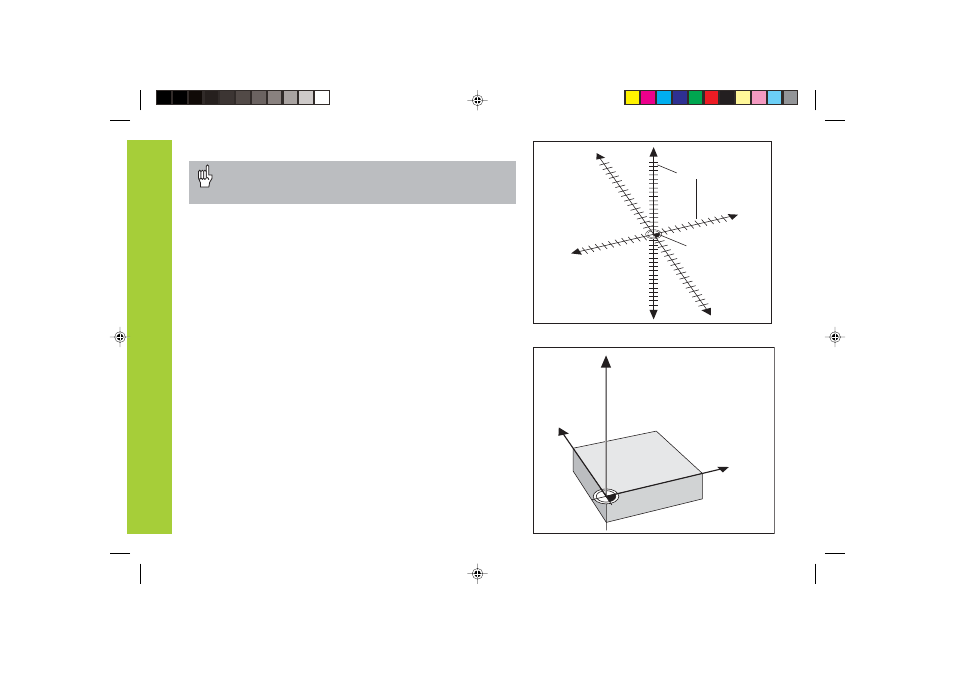
Coordinate system
The Cartesian
1)
coordinate system is used to describe the geometry of
a workpiece. The Cartesian coordinate system consists of three
mutually perpendicular axes X, Y and Z. The point of intersection of
these axes is called the datum or origin of the coordinate system.
Think of the axes as scales with divisions (usually in millimeters) which
allow us to fix points in space referenced to the datum.
To determine positions on a workpiece, the coordinate system is
laid onto the workpiece.
The machine axes are parallel to the axes of the coordinate system.
The Z axis is normally the tool axis.
1)
Named in honor of the French mathematician and philosopher
René Descartes (1596 to 1650)
Bateil1.pm6
07.11.2001, 10:36
4