Rp discovery, Troubleshooting multicast routing and forwarding, Static multicast route failure – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 75
65
IMPORTANT:
IGMP must be enabled on the device that acts as the receiver-side DR. Otherwise, the receiver hosts
attached to the DR cannot join any multicast groups.
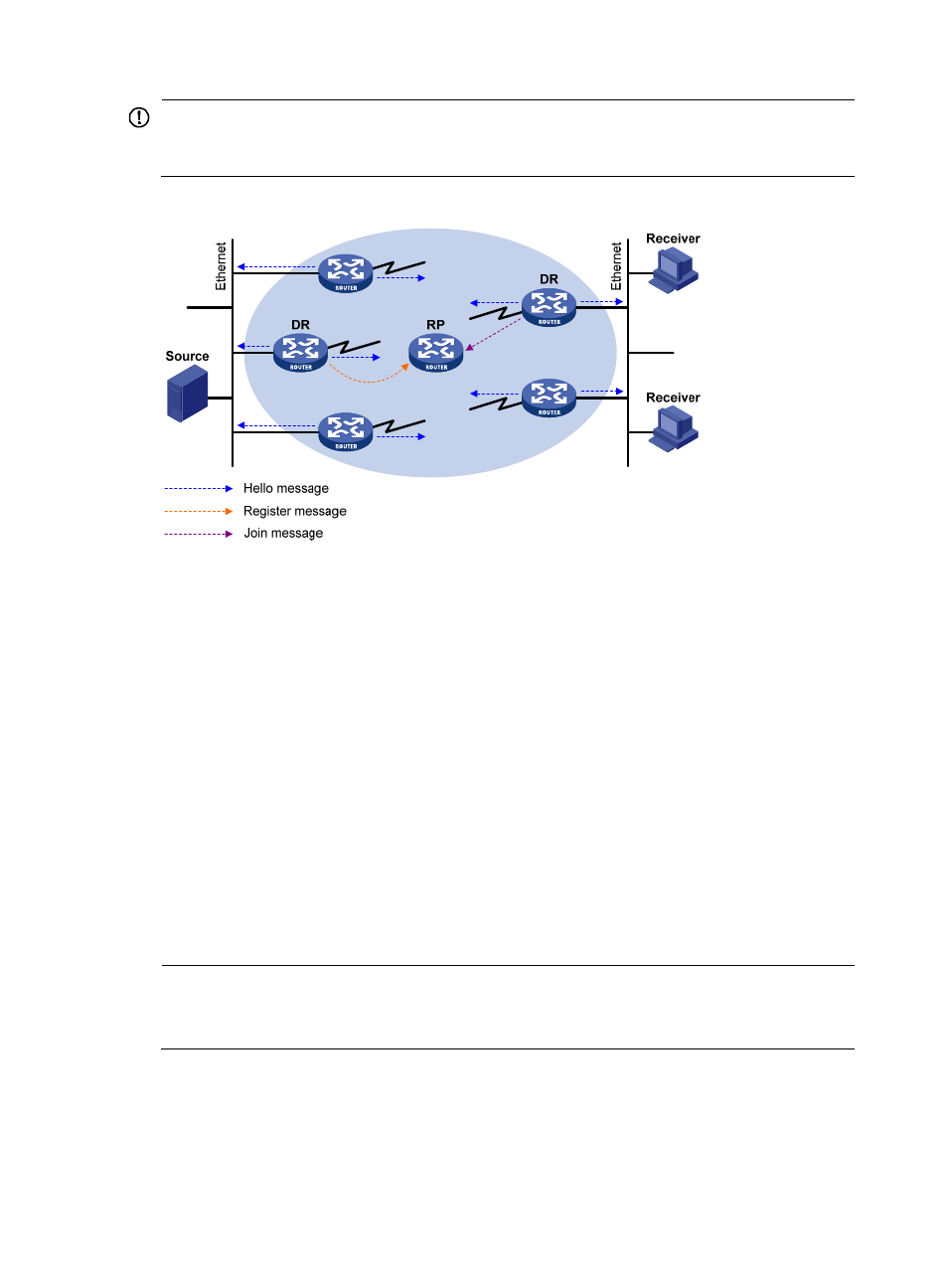
Figure 25 DR election
As shown in
, the DR election process is as follows:
1.
The routers on the shared-media LAN send hello messages to one another. The hello messages
contain the priority for DR election. The router with the highest DR priority is elected as the DR.
2.
In the case of a tie in the priority, or if any router in the network does not support carrying the
DR-election priority in hello messages, the router with the highest IP address wins the DR election.
If the DR fails, its PIM neighbor lifetime expires and the other routers will initiate to elect a new DR.
RP discovery
An RP is the core of a PIM-SM domain. For a small-sized, simple network, one RP is enough for multicast
forwarding throughout the network. In this case, you can specify a static RP on each router in the PIM-SM
domain. However, in a PIM-SM network that covers a wide area, a huge amount of multicast data is
forwarded by the RP. To lessen the RP burden and optimize the topological structure of the RPT, you can
configure multiple candidate-RPs (C-RPs) in a PIM-SM domain, and use the bootstrap mechanism to
dynamically elect RPs. An elected RP provides services for a different multicast group. For this purpose,
you must configure a bootstrap router (BSR). A BSR serves as the administrative core of a PIM-SM domain.
A PIM-SM domain has only one BSR, but can have multiple candidate-BSRs (C-BSRs) so that, if the BSR
fails, a new BSR can be automatically elected from the C-BSRs and avoid service interruption.
NOTE:
•
An RP can provide services for multiple multicast groups, but a multicast group only uses one RP.
•
A device can act as a C-RP and a C-BSR at the same time.
As shown in
, each C-RP periodically unicasts its advertisement messages (C-RP-Adv messages)
to the BSR. An advertisement message contains the address of the advertising C-RP and the multicast
group range to which it is designated. The BSR collects these advertisement messages and organizes the
C-RP information into an RP-set, which is a database of mappings between multicast groups and RPs. The
- H3C S9800 Series Switches H3C S5560 Series Switches H3C S5130 Series Switches H3C S5120 Series Switches H3C S12500 Series Switches H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module