Multicast source registration, Configuring igmp, Overview – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 77
67
1.
When a receiver wants to join the multicast group G, it uses an IGMP message to inform the
receiver-side DR.
2.
After getting the receiver information, the DR sends a join message, which is forwarded hop by
hop to the RP for the multicast group.
3.
The routers along the path from the DR to the RP form an RPT branch. Each router on this branch
adds to its forwarding table a (*, G) entry, where the asterisk (*) represents any multicast source.
The RP is the root of the RPT, and the DR is a leaf of the RPT.
When the multicast data addressed to the multicast group G reaches the RP, the RP forwards the data to
the DR along the established RPT, and finally to the receiver.
When a receiver is no longer interested in the multicast data addressed to the multicast group G, the
receiver-side DR sends a prune message, which goes hop by hop along the RPT to the RP. After receiving
the prune message, the upstream node deletes the interface that connects to this downstream node from
the outgoing interface list and determines whether it has receivers for that multicast group. If not, the
router continues to forward the prune message to its upstream router.
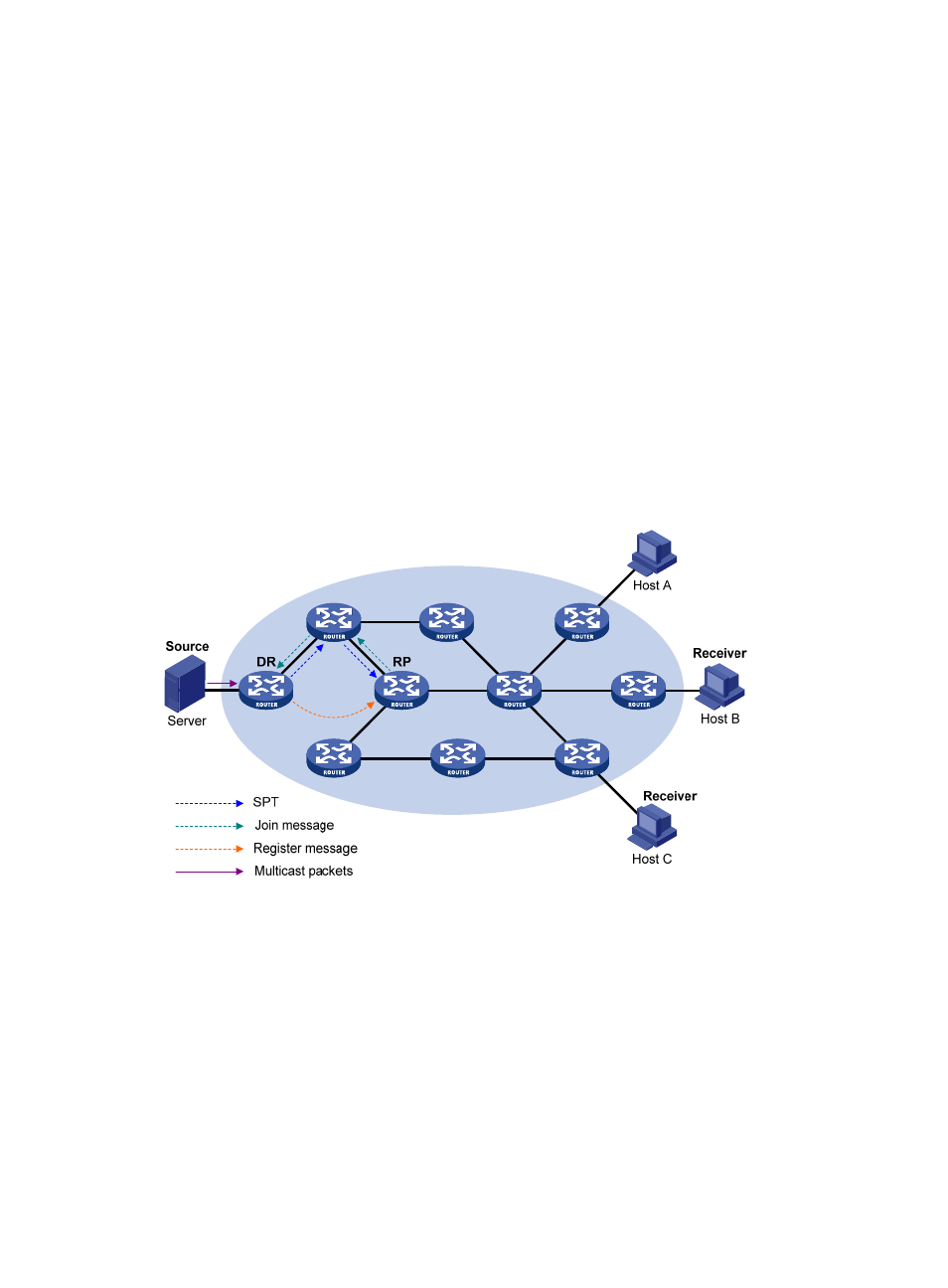
Multicast source registration
The multicast source uses the registration process to inform an RP of its presence.
Figure 28 Multicast source registration
As shown in
, the multicast source registers with the RP as follows:
1.
The multicast source S sends the first multicast packet to the multicast group G. When receiving the
multicast packet, the source-side DR encapsulates the packet in a PIM register message and
unicasts the message to the RP.
2.
After the RP receives the register message, it decapsulates the register message and forwards the
register message down to the RPT. Meanwhile, it sends an (S, G) source-specific join message
toward the multicast source. The routers along the path from the RP to the multicast source
constitute an SPT branch, and each router on this branch creates an (S, G) entry in its forwarding
table.
3.
The subsequent multicast data from the multicast source are forwarded to the RP along the
established SPT. When the multicast data reaches the RP along the SPT, the RP forwards the data
- H3C S9800 Series Switches H3C S5560 Series Switches H3C S5130 Series Switches H3C S5120 Series Switches H3C S12500 Series Switches H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module