Configuring gre, Overview, Gre encapsulation format – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 13
1
Configuring GRE
Overview
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a protocol designed for encapsulating and carrying the packets
of one network layer protocol (for example, IP or IPX) over another network layer protocol (for example,
IP). The path that transfers the encapsulated packets is referred to as a GRE tunnel.
A GER tunnel is a virtual point-to-point (P2P) connection. Packets are encapsulated at one end of the
tunnel and de-encapsulated at the other end.
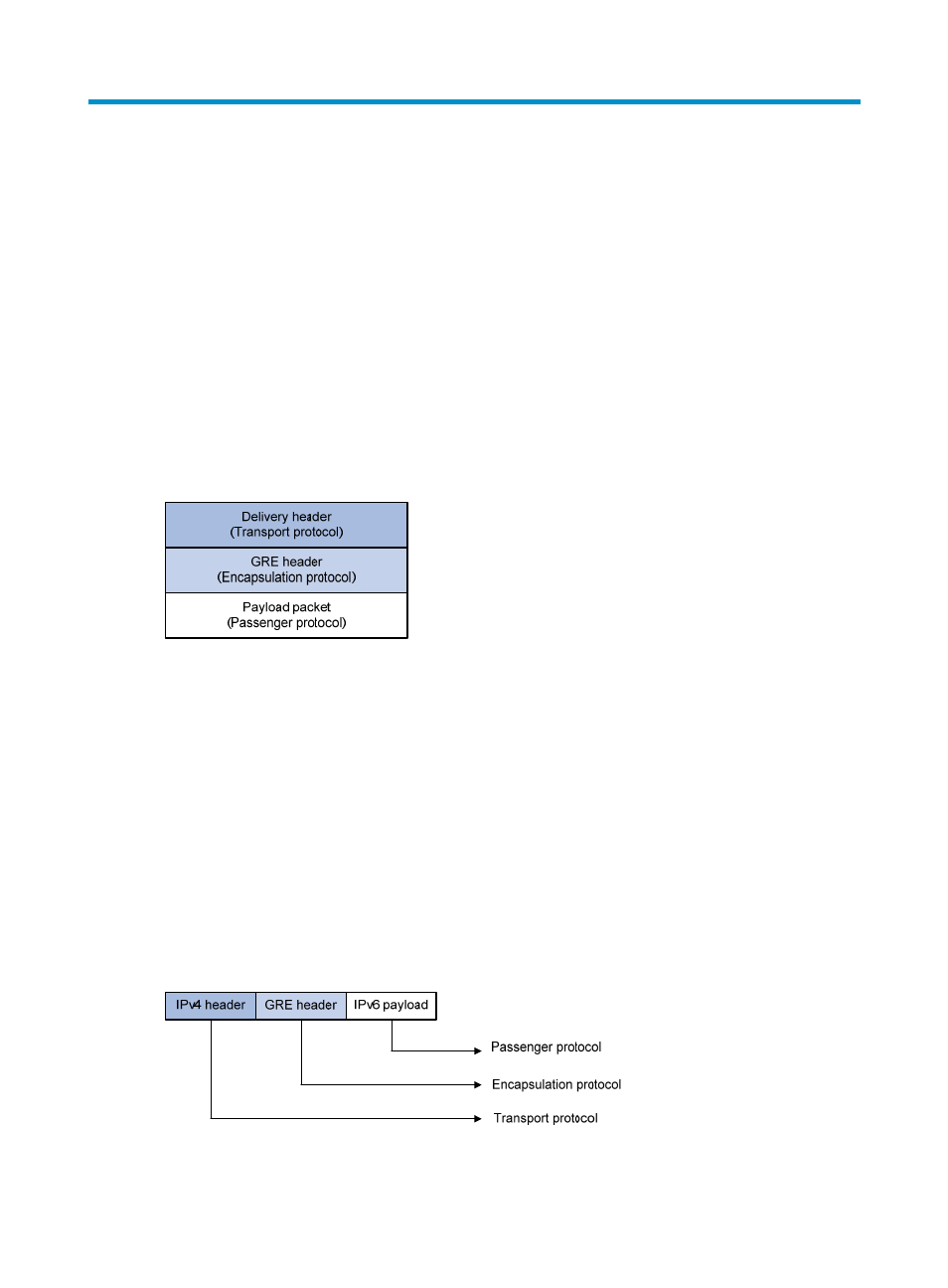
GRE encapsulation format
Figure 1 GRE encapsulation format
As
shows, a GRE-tunneled packet comprises the following parts:
•
Payload packet—the packet to be encapsulated and transmitted. The protocol type of the payload
is called the passenger protocol.
•
GRE header—After the system receives a payload packet, it adds a GRE header to the payload
packet, so that the payload packet can be transferred as a GRE packet. The GRE protocol, which
encapsulates the payload packet, is called the encapsulation protocol.
•
Delivery header—The protocol used to transfer the GRE packet over the network is called the
delivery protocol or transport protocol. The system adds a transport protocol header to the GRE
packet to deliver it to the tunnel end.
For example, to transfer an IPv6 packet over an IPv4 network through a GRE tunnel, the system
encapsulates the IPv6 packet in the format shown in
. The passenger protocol is IPv6, the
encapsulation protocol is GRE, and the transport protocol is IPv4.
Figure 2 Format of a GRE-encapsulated packet
Depending on the transport protocol, GRE tunnels have the following tunnel modes:
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS