Mesh warp effect mirror effect, Mesh warp effect, Mirror effect – Adobe After Effects User Manual
Page 532
Blending Mode
Resize Layer
Rows, Columns
Quality
Distortion Mesh
Note:
Reflection Center
Reflection Angle
The blending mode used to combine the magnified area with the original layer. The None option displays transparent pixels
around the magnified area.
If Resize Layer is selected, the magnified area can extend beyond the boundaries of the original layer.
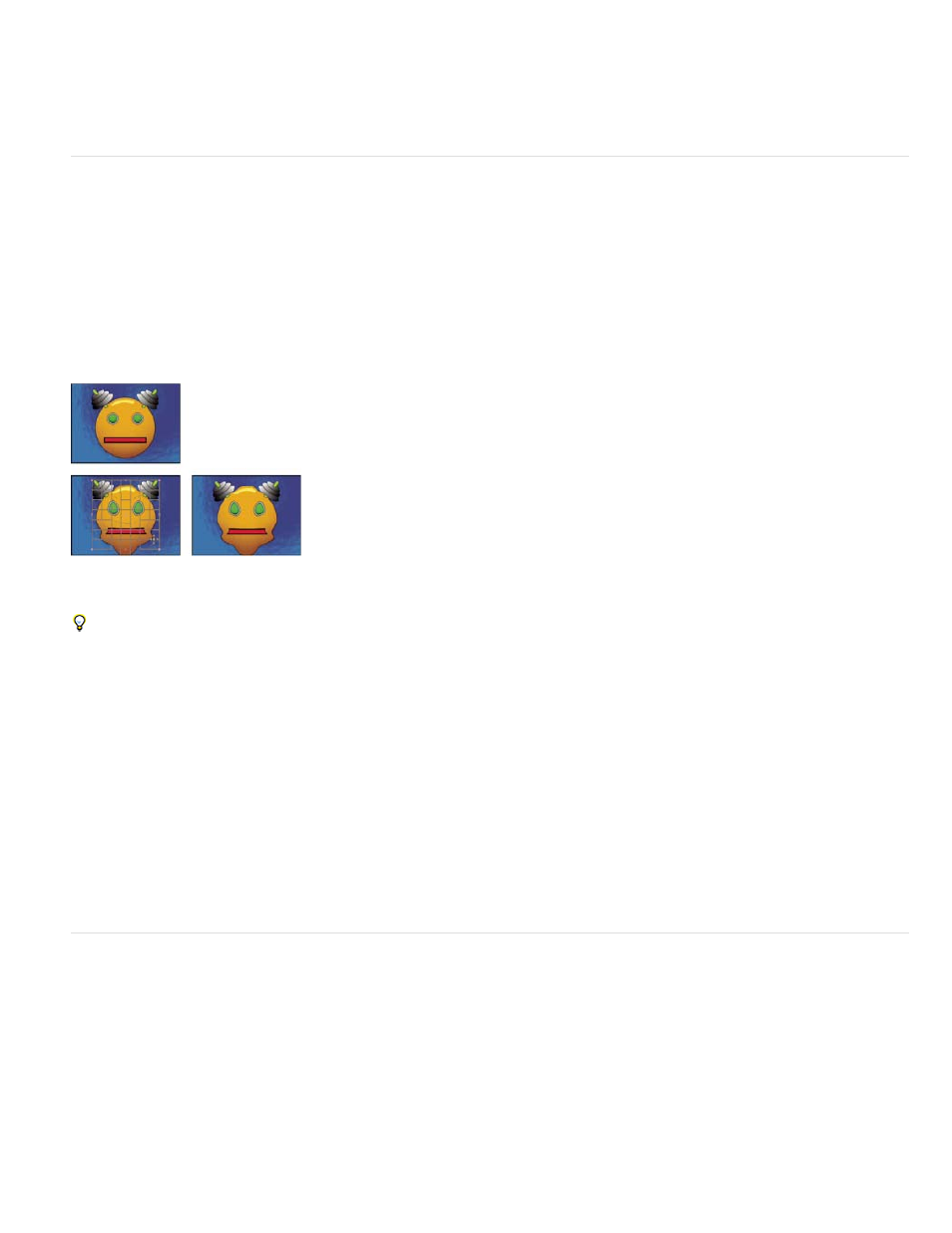
Mesh Warp effect
The Mesh Warp effect applies a grid of Bezier patches over a layer, which you can manipulate to distort areas of an image. Each corner of a
patch includes a vertex and two to four tangents (points that control the curvature of the line segment that makes up the edge of the patch). The
number of tangents depends on whether the vertex is in a corner, on an edge, or inside the grid. By moving the vertices and tangents, you can
manipulate the shape of the curved line segment. The finer the grid, the tighter the adjustments you can make to the area of the image inside the
patch.
The Mesh Warp effect is commonly used to morph a pair of images to create a transition from one image to another.
This effect works with 8-bpc and 16-bpc color.
Original (upper-left), with distortion mesh (lower-left), and with Mesh Warp applied (lower-right)
To select multiple vertices, Shift-click the vertices.
Specify up to 31 patches vertically (Rows) or horizontally (Columns). For broader distortion, use fewer patches. For finer control,
use more. Drag the vertices and tangents to change the grid shape. The image follows the grid shape according to the elasticity setting and the
boundary created by the adjacent patch.
Specifies how closely the image follows the shape defined by the curve. The higher the quality value, the more closely the image follows
the shape. Higher quality settings require more rendering time.
Click the stopwatch to animate the distortion over time.
Each patch becomes a boundary for the distortion. For example, when you stretch a patch, the area of the image in the patch stretches,
squishing the area of the image in the adjacent patch. The boundary of the adjacent patch protects the image inside it from being squished to
zero. In other words, you can’t push an image out of its patch.
Mirror effect
The Mirror effect splits the image along a line and reflects one side onto the other.
The position of the line about which the reflection occurs.
The angle of the line about which the reflection occurs. An angle of 0° reflects the left side onto the right. An angle of 90°
reflects the top onto the bottom.
This effect works with 8-bpc and 16-bpc color.
528